In the past decade, microcellular foaming process applied in reciprocal injection molding process has been well developed, and the patented commercial process is well known as MuCell® process. This processing technology is widely used in automotive, consumer, and industrial applications. The practice of blending supercritical fluids with molten polymer in the plasticizing stage following by a complicated cell nucleation and growing mechanism in the filling stage reduces the product weight without compromising mechanical properties, and mechanical property like compact resistance is normally enhanced.
 |
 |
Combining microcellular process with fiber or nanocomposite material, product designer can manipulate material varieties to fit their proper product quality criteria. For example, foaming process can reduce the flow-induced fiber orientation which causes anisotropic mechanical properties of fiber material injection-molded parts. Random fiber distribution is also desired to prevent non-uniform part warpage or shrinkage.
In order to determine the performances of injection-molded parts and aid the design of the mold, part, and the processing conditions, the foaming behavior must be accurately predicted. Moldex3D’s new microcellular injection molding module featured in Moldex3D R11 offers a new solution in determining the cell nucleation and cell growing of foaming process. Prior foaming simulation assumes certain amount of cell nucleation number and an uniform cell density distribution within molded product. The results based on these assumptions deviate from real molded part seriously. Moldex3D R11 employs realistic cell nucleation and growing models describing the competition phenomena of these two behaviors during foaming process. Features include: cell size distribution, cell number distribution, weight reduction, etc. The experimental validation is as illustrated in Figure 1. You can find out more detailed microcellular foaming dynamics with experimental validation in one of our technical papers presented in the Conference Paper section of this issue.
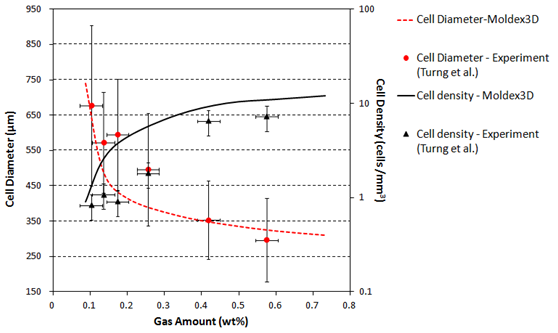 Fig. 1 Comparison of calculated and experimental data of cell sizes and densities for LDPE/N2 system.
Fig. 1 Comparison of calculated and experimental data of cell sizes and densities for LDPE/N2 system.
(Y-axis error bar is a guess value of 30% of lowest experimental gas concentration 0.1 wt%)
With Moldex3D’s latest technology in microcellular injection molding simulation, designers and molders can gain a complete insight into control of foaming process, and further for their process design and product quality. For more information regarding microcellular injection molding and case studies, please go to our website www.moldex3d.com to learn about our exciting new simulation technology.
